How Stainless Steel Is Made

HOW STAINLESS STEEL IS MADE
Introduction To Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an iron-based alloy, primarily alloyed with Chromium, and Nickel in some cases. An alloy is a material made up of two or more chemical elements. Stainless Steel has a wide range of applications ranging from daily use Utensils to Nuclear and Aerospace engineering. It has excellent resistance to stain or rust due to its chromium content. There are hundreds of stainless steels grades and variants available, in addition to many exclusive and proprietary alloys produced by different stainless steel producers.
The applications of these wide ranges of grades are almost endless: medical equipment, exterior architectural designing, decorative interior designing, bulk materials handling equipment, roofing, automobile components (exhaust, trim/decorative, engine, chassis, fasteners, tubing for fuel lines), chemical processing plants (scrubbers and heat exchangers), dairy and chemical (acidic/alkaline) storage units, pulp and paper manufacturing, petroleum refining, water, and oil supply piping, consumer products, marine and shipbuilding, pollution control, sporting goods (snow skis), and transportation (rail cars), to name just a few.
Types Of Stainless Steel
There are several types of Stainless Steels categorised on basis of their microstructure. The commerical ones are listed below.
- Austenite
- Face Centred Cubic Crystal Structure. Absorbs more Carbon than Ferrite Crystals.
- Ferrite
- Body Centred Cubic Crystal Structure. Ferrite crystals with very low amount of Carbon.
- Martensite
- Body Centred Cubic Crystal Structure. Formed by quenching heated Austenite.
- Duplex
- Contains equal amount of Austenite and Ferrite
- Precipitation Hardened
- Strengthened Alloys by quenching and ageing. Semi-Austenite and Semi-Martensite Properties.
Raw Materials For Manufacturing
Manufacturing Process Of Stainless Steel
MELTING
CASTING
FORMING
HEAT TREATMENT
DESCALING
CUTTING

FINISHING
INSPECTION
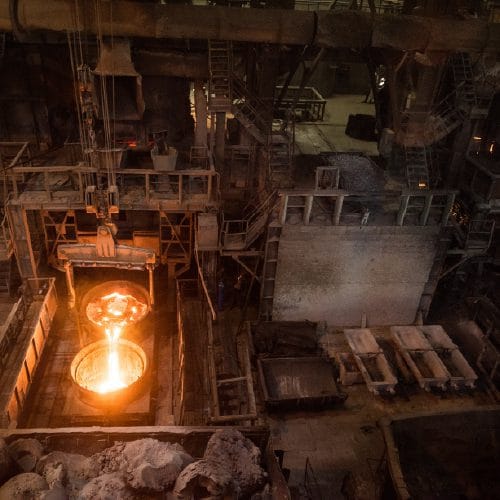
1) Melting: The Magic Of Metallurgy
Melting is basically the process of heating the raw materials and adding them to the ladle in a pre-planned manner to derive the alloyed metal, which is Stainless Steel. There are various byproducts of the process like slag and emitted gases. The primary options for melting are Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) which primarily uses scrap as the raw material and Basic Oxidation Furnace (BOF) which uses ores and compounds as the raw materials.
Melting is a complex process and it is always done under strict observation of the manufacturing teams. Mastering precise control and critical timing is the key to deriving the desired outcome. This Stainless Steel Manufacturing process can take anywhere between 5 hours to 12 hours depending on the desired outcome.
2) Casting: The Semi-Finished Form
The melted alloy is then poured out of the ladle and cast into the desired semi-finished form of Blooms (large rectangular bars), Billets (large rounded cornered square bars), Slabs (thick sheets with skelp width), Rods (large round bars), or Tube Rods (rods for further processing of seamless tubes and pipes). These semi-finished products are then either shipped for further processing or sold to rolling mill manufacturers who will further process them. In some manufacturing units, the adopted process can be continuous casting which would output the cast molten to the rolling machine (to manufacture coils) or drawing machine (to manufacture bars and rods), skipping the semi-finished form.
3) Forming: Shaping The Output
Forming process shapes the semi-finished billet, bloom, slab, or rod into the desired output. Each semi-finished product has a specific advantage in forming a certain type of product. Slabs are the best choice to form Coils and Plates, Billets are the best choice to form Rods and Bars. Depending on the desired outcome, a unique set of manufacturing processes is adopted. The Coils will be processed by Rolling, Seamless Pipes will be processed by Drawing, and as such other processes.
4) Heat Treatment: Strengthening The Output
Heat treatment is how stainless steel achieve their strong mechanical properties. Heat treatement helps to relieve internal stress created in the forming process. The material is treated with high tempretures of heat depending on composition. The crystal structures can be controlled with heat treatement which can in turn used to improve the properties depending on the crystal and steel type. Processes like ageing and quenching are adopted as per the desired output to further improve the properties of the metal.
5) Descaling: Clearing The Surface
The heat-treated material undergoes a whole lot of chemical and physical change. Annealing the metal causes a scale or build-up to form on the stainless steel material. The scale can be removed using several commercial processes. One of the most common methods is pickling. Pickling uses a nitric-hydrofluoric acid bath on the scale to make the surface scale-free. Electro cleaning is another commonly used method. An electric current is applied to the surface using a cathode and phosphoric acid. The annealing and descaling processes occur at different stages of stainless steel manufacturing depending on the type of grade being worked.
6) Cutting: Slicing As Per Desired Size
Cutting is the process of obtaining the desired size of the final product while eliminating or scrapping the excess. Different methods of cutting can be applied depending on the product. A coil can be trimmed using High Speed Steel blades or shearing. Flame cutting and Plasma cutting can also be adopted for faster and efficient cutting.
7) Finishing: Processing The Stainless Surface
The product can then finally be processed for the surface finishing. Each type of prodct has a different types of finishes available. Rods can have Black or Bright finishes, Coils can have a No.1 or 2B finish, Pipes can have a Polished or Standard finish. The material can also be processed with advanced finishes like 8K Mirror or Matte finish which is majorly used for decorative applications.
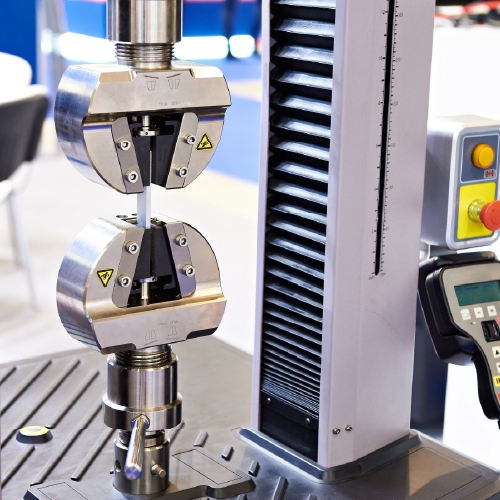
8) Inspection: Critical Quality Checks
After a long manufacturing process of metallurgy the material undergoes thorough observation and inspection. The material is tested chemically, mechanically and physically. After successful tests the material is issued a Test Certificate which is the seal of its quality. Some materials are even marked with their batch number and test certificate number for further assurance of genuinity for sale. The long process of how stainless steel is made comes to an end after packaging and shipping off to the customers.
How Stainless Steel Is Made: The Conclusion
The manufacturing process of how stainless steel is made, is an ever-improving process. Every year there are new tweaks and improvements that produce better quality material and a faster rate. The demand for Stainless Steel grows every year across the globe, and to keep up with the demand these innovations and improvements are born.
THANK YOU
DON'T MISS ON LATEST ARTICLES!
SIGN UP NOW!













